This malware, according to CYFIRMA, is extremely difficult to identify and eliminate due to its advanced encryption, evasion strategies, and boot-level persistence.
NNice encrypts files with the “.xdddd” an extension and leaves a ransom note requesting cash to decode them, targeting Windows PCs. Here are some things you should know to safeguard your systems against this escalating danger.
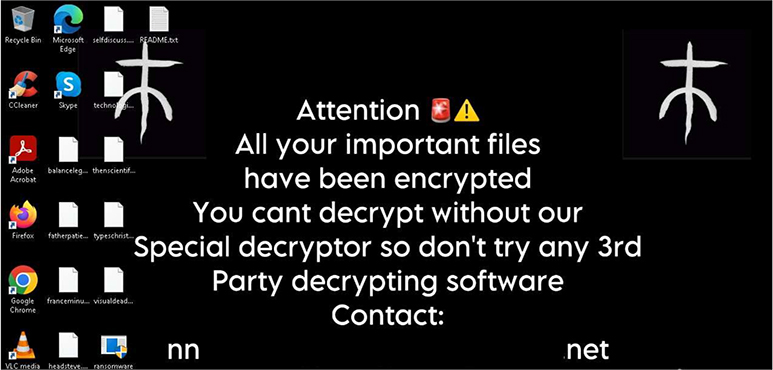
Researchers claim that Windows systems are the target of this new virus. Once on the victim’s computer, the ransomware encrypts data by attaching the “.xdddd” extension to the original filenames.
A ransom note called “Readme.txt,” which includes recovery instructions for files, is left behind.
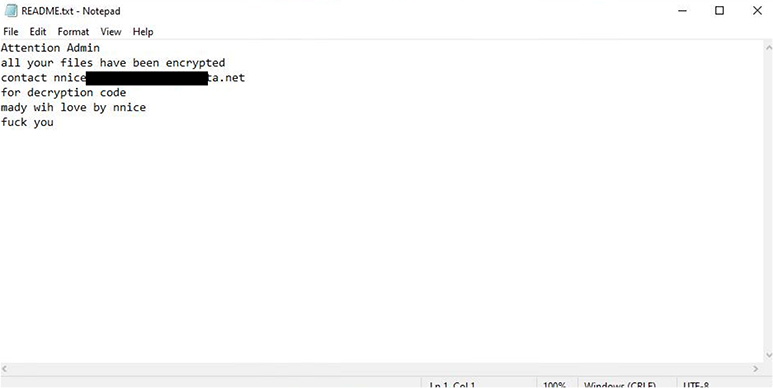
The malware modifies the wallpaper as shown below after encrypting the file. The sample has wide attack capabilities, including the ability to steal credentials and online session cookies, collect emails, and find security software.
It can sideload DLLs, bypass sandboxes, compromise defences, elevate privileges, impersonate, inject processes, and much more.
Similar to previous advanced ransomware strains, this strategy uses asymmetric encryption (RSA-2048) for key management and the speed of symmetric encryption (Salsa20) for bulk data encryption.
Researchers from CYFIRMA have discovered a number of MITRE ATT&CK strategies that Nnice employs, such as:
- T1486: Impact-Proof Encrypted Data
- T1490: Prevent System Recuperation
- T1055: Injection of Process
- T1562: Undermine Protections
- T1070: Elimination of Indicators
To reduce the likelihood of ransomware attacks, cybersecurity experts advise putting in place reliable backup systems, updating software, and using sophisticated threat detection technologies.
Nnice exhibits advanced evasion strategies, such as the capacity to terminate services and end programs that could obstruct file encryption.
In order to confuse debugging tools, it also generates child processes that imitate genuine system services in order to blend in with regular operations.
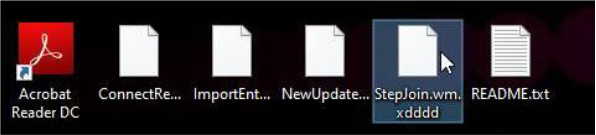
Organisations are recommended to keep an eye on and block the ransomware’s identified SHA-256 hash, 4dd08b0bab6f19d143cca6f96c8b780da7f60dbf74f1c16c3442bc9f07d38030, in order to reduce risks.
Adopt a zero-trust design and use robust authentication techniques, such multifactor authentication (MFA), for all vital systems.