~Hackingblogs: Research Exposes KT Corporation’s Involvement in the Torrent Malware Issue
KT Corporation Scandal
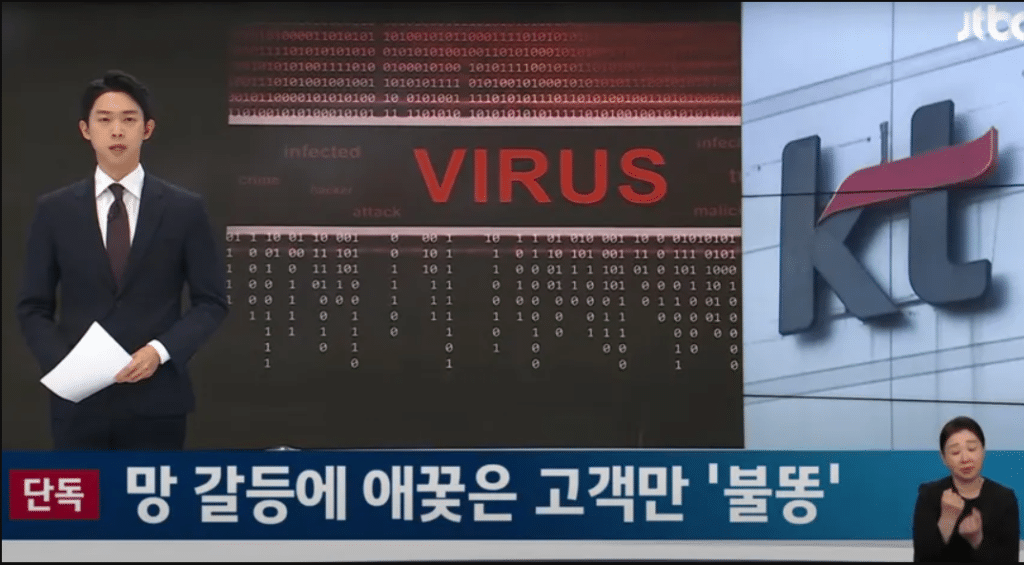
Leading South Korean news outlet JTBC recently carried out a comprehensive investigation of KT Corporation, one of the biggest telecom service providers in the nation. There have been claims that KT deliberately infected over 600,000 people with malware as a result of their usage of torrent services.
Users of Webhard, a well-known Korean cloud service provider, started reporting mysterious issues, which led to the discovery of the problem. Webhard’s grid programme, which relies on peer-to-peer file sharing via BitTorrent, was found to have been hacked.
“There is suspicion of a hacking attempt on our service, which is particularly destructive and disruptive,” stated a Webhard representative who wished to remain anonymous.
Subsequent investigation inside the organisation uncovered a concerning fact: most impacted users were KT internet service provider (ISP) subscribers.
So, what affects consumers’ PCs does this spyware cause? It modifies files to become invisible, generates mysterious directories, and in certain instances, totally disables the Webhard programme and the impacted PCs.

Legal authorities in South Korea have claimed that KT could have broken many local laws, including as the Information and Communications Network Act and the Protection of Communication Secrets Act. Consequently, since last November, 13 people—including KT employees and subcontractors who were allegedly involved in the malware attack—have been discovered and prosecuted. The inquiry is still being conducted.
KT justified its actions by claiming that it had used the virus to take control of an application that it described as harmful to Webhard grid service subscribers. However, the installation of malware without users’ consent—an unlawful act—rather than the usage of the Webhard BitTorrent protocol is the main topic of dispute.

While some opponents contend that files were distributed using torrent apps, KT’s participation raised privacy concerns since it specifically targeted customers involved in torrent activity.
Disappointedly, KT chose to spread malware rather than alert or terminate people using peer-to-peer services on their network.
Considering these incidents, many are wondering how KT was able to infect their computers with malware without their permission or awareness.
As the inquiry progresses, it will become clearer how complicated the relationships are in the digital era between internet service providers, user privacy, and legal obligations.
Frequently Asked Question
- What is the dispute around the torrent malware from KT Corporation?
The dispute centres on claims that Webhard, a well-known Korean cloud service provider, allowed over 600,000 customers to access torrent services, so inadvertently infecting them with malware. KT Corporation is a significant South Korean ISP. - How was this disagreement discovered?
BitTorrent peer-to-peer file sharing is used by Webhard’s grid programme, and users started experiencing mysterious issues and disturbances when using it. Later, an examination found that malware was the root of these problems. - How did the infection affect the computers of the users?
According to reports, the virus that KT Corporation implanted made files invisible, concealed directories, and in extreme situations, rendered customers’ computers and the Webhard programme inoperable. - Which legal matters are at stake in this dispute?
By putting malware on consumers’ computers without permission, KT Corporation is suspected of breaking many laws in South Korea, including the Information and Communications Network Act and the Protection of Communication Secrets Act. - In what way has KT Corporation addressed these accusations?
In an attempt to justify its actions, KT Corporation stated that it was trying to take control of a programme that it believed was harmful and was impacting Webhard grid service subscribers. Critics counter that it is still unlawful to install malware without the user’s permission. - Who has been connected to this dispute?
Thirteen people, including KT employees and subcontractors who were reportedly engaged in the malware deployment last November, have been identified and charged by legal authorities thus far. The inquiry is still on. - What possible repercussions may KT Corporation face?
If proven guilty, KT Corporation may be subject to fines and reputational harm. Affected users may also file a claim for reimbursement for losses brought on by the infection. - What other options would KT Corporation have looked at before using malware?
KT Corporation may have taken various steps to reduce excessive bandwidth use from torrent sites, protecting user privacy and legal limits, before turning to virus deployment. - How is internet consumers’ confidence in ISPs affected by this controversy?
This dispute raises questions about ISPs’ obligations to protect user privacy and the techniques they use to control network traffic. Users’ confidence in how KT Corporation and other ISPs handle comparable problems may be impacted. - How can users safeguard themselves against such occurrences?
By utilising trustworthy antivirus software, maintaining system updates, and exercising caution while downloading files from unidentified sources or participating in behaviours that can provoke hostile behaviour from ISPs, users can improve their security.